数组 Array
数组是按特定顺序排列的多个元素,通常都是相同类型的元素(但在 JS 里可以不同)。
使用整数索引访问元素以指定所需的元素。数组可以是固定长度的,也可以是可调整大小的。
链表 LinkedList
链表,也叫列表,是任何类型的数据元素的线性集合,每个元素称为节点,其中每个节点都有自己的值,并指向链表中的下一个节点。
与数组相比,链表的主要优点是始终可以有效地插入和删除值,而无需重新定位列表的其余部分。然而,某些其他操作(例如对某个元素的随机访问)在链表上比在数组上慢。
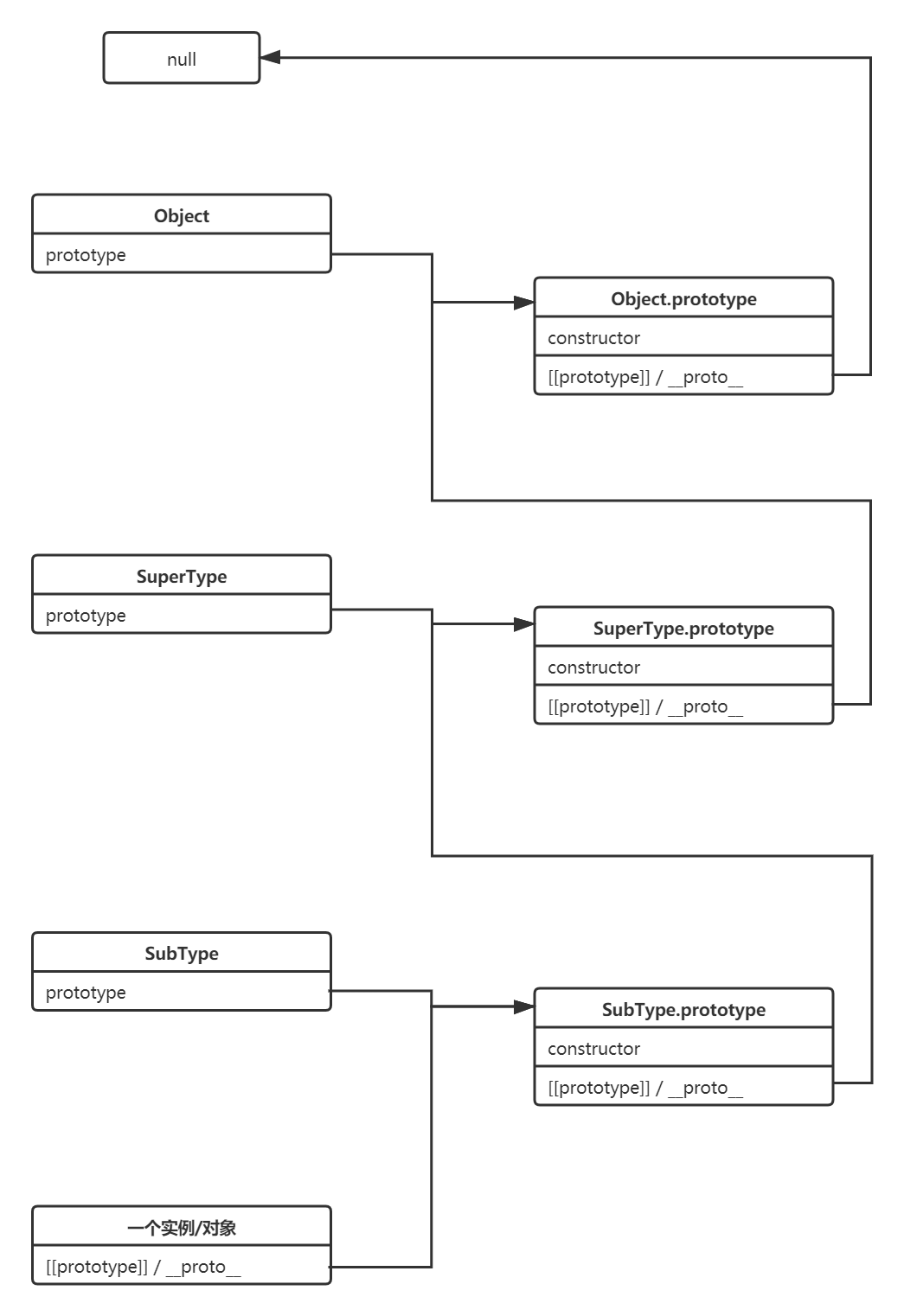
在 JS 中,最常见的链表就是对象的原型链结构:一个对象实例具有__proto__属性,其指向初始化其类型的prototype属性,而prototype本身也具有__proto__属性,最终这种继承关系指向null。
instance.__proto__ === SubType.prototype;
instance.__proto__.__proto__ === SuperType.prototype;
instance.__proto__.__proto__.__proto__ === Object.prototype;
instance.__proto__.__proto__.__proto__.__proto__ === null;
单链表
双链表
队列 Queue
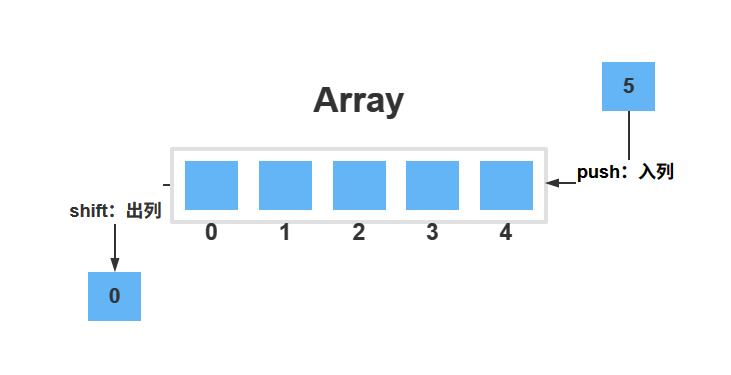
先进先出(FIFO,first in first out)队列,简称为队列。队列支持以下操作:
- 入列:添加元素到队列末尾,相当于数组的
push操作 - 出列:删除开头元素,相当于数组的
shift操作 - 获取队列开头和末尾的元素
- 获取队列长度
实现参考:Queue - The Algorithms (the-algorithms.com)
class Queue {
#size
constructor () {
this.head = null
this.tail = null
// 队列长度
this.#size = 0
return Object.seal(this)
}
get length () {
return this.#size
}
/**
* @description - 往队列末尾添加元素
* @param {*} data
* @returns {number} - 返回队列新的长度
*/
enqueue (data) {
const node = { data, next: null }
if (!this.head && !this.tail) {
this.head = node
this.tail = node
} else {
this.tail.next = node
this.tail = node
}
return ++this.#size
}
/**
* @description - 移除队列开头元素
* @returns {*} - 返回被移除的元素
*/
dequeue () {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw new Error('Queue is Empty')
}
const firstData = this.peekFirst()
this.head = this.head.next
if (!this.head) {
this.tail = null
}
this.#size--
return firstData
}
/**
* @description - 返回队列开头的元素
* @returns {*}
*/
peekFirst () {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw new Error('Queue is Empty')
}
return this.head.data
}
/**
* @description - 获取队列末尾的元素
* @returns {*}
*/
peekLast () {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw new Error('Queue is Empty')
}
return this.tail.data
}
/**
* @description - 队列转换成数组
* @returns {Array<*>}
*/
toArray () {
const array = []
let node = this.head
while (node) {
array.push(node.data)
node = node.next
}
return array
}
/**
* @description - 队列是否为空
* @returns {boolean}
*/
isEmpty () {
return this.length === 0
}
}
export default Queue
栈 Stack
堆栈是一种基本的线性数据结构,它遵循访问对象的顺序。这种顺序称为后进先出(LIFO)或先进后出(FILO,First In Last Out),要正确区分栈顶的概念:
警告
栈顶:相当于数组结尾的元素。
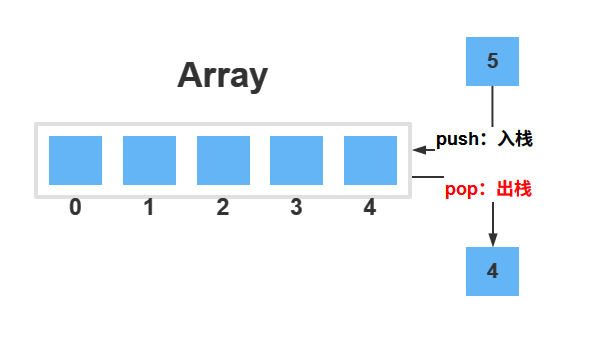
栈支持以下操作:
- 入栈:添加元素到栈顶,相当于数组的
push方法 - 出栈:从栈顶删除元素,相当于数组的
pop方法 - 获取栈顶元素,相当于获取数组的最后一个元素
class Stack {
private stack = [];
private limit;
/**
* constructor of the stack, can set a limit, if not provided there is no limit to the stack.
* @param {number} [limit=Number.MAX_VALUE] the limit of the stack
*/
constructor(limit = Number.MAX_VALUE) {
this.limit = limit;
}
/**
* @function push
* @description - adds a new element to the stack
* @param {T} value - the new value to add
*/
push(value) {
if (this.length() + 1 > this.limit) {
throw new Error('Stack Overflow');
}
this.stack.push(value);
}
/**
* @function pop
* @description - remove an element from the top
* @throws will throw an error if the stack is empty
* @return {T} removed element
*/
pop() {
if (this.length() !== 0) {
return this.stack.pop() as T;
}
throw new Error('Stack Underflow');
}
/**
* @function length
* @description - number of elements in the stack
* @return {number} the number of elements in the stack
*/
length() {
return this.stack.length;
}
/**
* @function isEmpty
* @description - check if the stack is empty
* @return {boolean} returns true if the stack is empty, otherwise false
*/
isEmpty() {
return this.length() === 0;
}
/**
* @function top
* @description - return the last element in the stack without removing it
* @return {T | null} return the last element or null if the stack is empty
*/
top() {
if (this.length() !== 0) {
return this.stack[this.length() - 1];
}
return null;
}
}