Redux入门
什么是 Redux
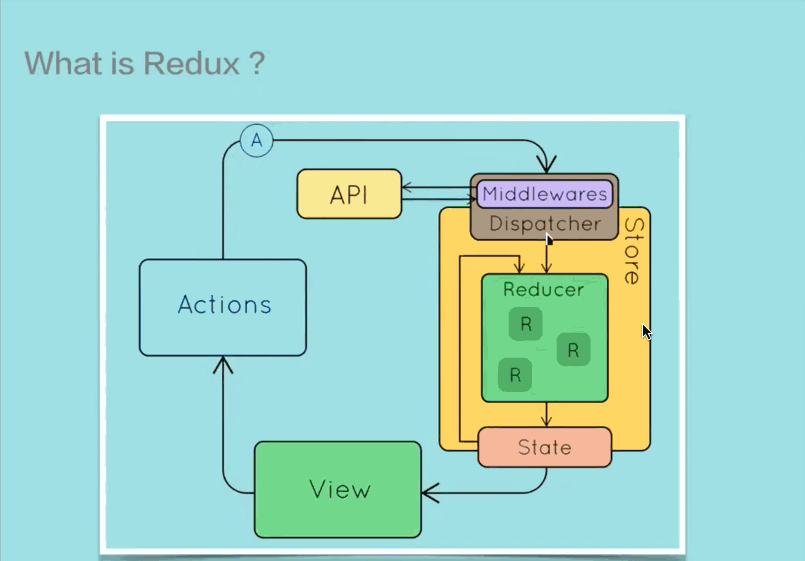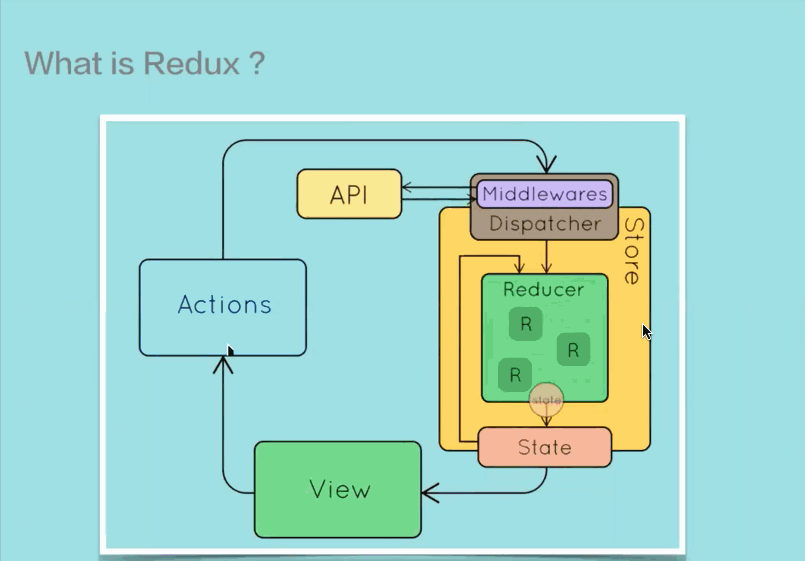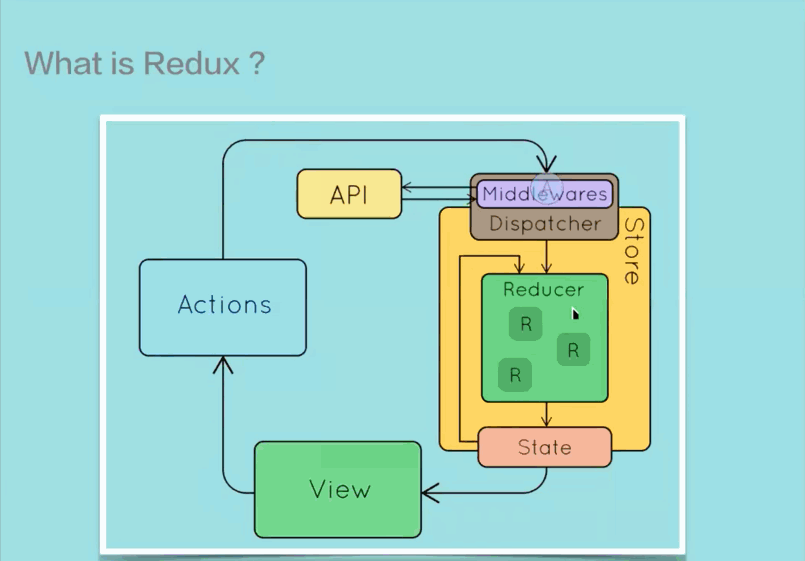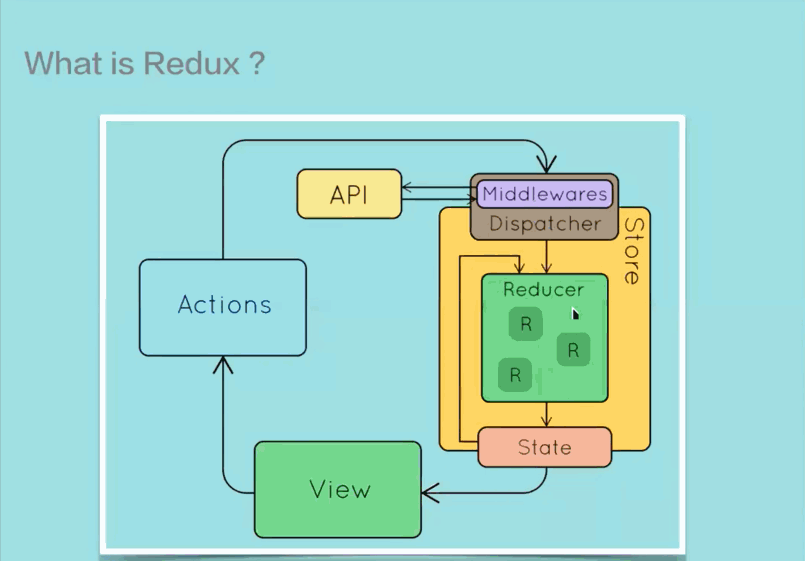
Redux 是一个 JavaScript 状态容器,提供可预测化的状态管理。不光能用于 React,也能用于其它 JS 库。它的大小只有 2KB 左右,非常得轻量。
Redux 提供了一种将 UI 和数据分离的机制,个人感觉其实和 MVC 差不多
Action
需要注意的时,在 Redux 中Action 是一个对象,表示数据的操作类型和携带的数据本身,将其送往store进行处理。也就是说在 Redux 中不存在props和state的概念了,所有的数据通过 Action 进行传送。
Action 通常具有数据操作类型名称和携带的数据本身,例如添加一条待办事项的 Action 如下:
{
type: "ADD_TODO",
payload: {
id: 1,
value,
},
}
可以使用一个负责生成的action的函数,这样就可以将数据操作完全的从页面剥离开,不用在 UI 组件中去生成 Action,这样做可以使代码层次更清晰;比如点击添加待办事项按钮onClick,通过 Action 生成函数可以产生一个type:"ADD_TODO"的 Action 对象
let todoId = 0;
//创建action
export const addTodo = value => ({
type: 'ADD_TODO',
payload: {
id: ++todoId,
value,
},
});
Reducer
Reducer 时真正负责管理state的纯函数,它负责接受当前state以及 Action,通过判断 Action 的类型,决定执行什么样的操作去修改state并返回新的state。
Reducer 可以拆分,最后再通过combineReducers函数将它们合并然后传入 Store 中
Note: 尤其需要注意的一点是Reducer 中修改 state 的操作要保证 immutable,对于深层嵌套的 state,一定要深拷贝
例如,在添加一条代办事项后,组装的 Action 对象会被送到 Reducer 特定的函数这里:
const initState = {
todoList: [],
};
export default function(state = initState, action) {
switch (action.type) {
// 判断Action的操作类型
case 'ADD_TODO': {
const { id, value } = action.payload;
// 返回新的state
return {
todoList: [
...state.todoList,
{
id,
value,
isComplete: false,
},
],
};
}
default:
return state;
}
}
Store
Store 在 Redux 中是一个中心管理器,它使用createStore函数根据特定的 Reducer 生成,负责将 Action 派发到 Reducer,同时将 Reducer 产生的新的state以props的形式传入组件内部。
import { createStore } from 'redux';
import reducer from '../reducers';
export default createStore(reducer);
页面组件发生交互事件,会产生 Action,而页面组件无法直接将 Action 送往 Reducer 去处理,它需要通过store.dispatch(action)来分发 Action 给 Reducer;而当 Reducer 处理完了以后,Reducer 也无法将state直接给组件,所以组件需要通过store.subscribe(listener)来订阅state的更新。
middleware
middleware 提供的是生成 Action 以后,在到达 Reducer 之前的功能拓展,所以可以使用 middleware 来进行调用异步接口,日志记录等功能开发。
在传统的 Redux 使用过程中,Action 只是一个对象,当组件生成 Action 以后,只能同步传递到 Store 中处理。有了 middleware,就可以在 Action 处理之前执行一些异步操作,让 Action 延迟分发到 Store 的过程,在等到一定延迟以后再将 Action 发送到 Store 去处理。
React-Redux
React Redux 是基于 React 的Context对 Redux 的进一步封装,提供共享的全局状态管理机制。
安装
React Redux 需要配合 Redux 一起使用
yarn add redux react-redux
API
React Redux 使用部分 Redux 的 API,同时封装了自己的 API
Provider
<Provider store={store}>使用 React 的Context提供全局store共享的机制。Context提供的是在跨越组件层级的共享数据管理机制,对于某些需要全局共享的状态,例如登录用户信息,用户主题等,使用Context做到全局共享是最简单的方式。
使用Context的方式如下:
- 首先在组件外部创建
Context,允许后传入一个默认值;然后将顶层组件通过Context.Provider包裹起来,并设置传递的值
import React from 'react';
export const UserContext = React.createContext();
export default function() {
return (
<UserContext.Provider value={'皮皮虾'}>
<Root />
</UserContext.Provider>
);
}
- 记得生成
Context以后要导出,这样其它组件可以通过import获取Context共享的值 - 其他组件在通过
import引入Context以后,可以使用Context.Consumer来订阅 context 的变化,Context.Consumer内部必须是一个函数作为子元素,这个函数接收当前的 context 值,并返回一个 React 节点
<ThemeContext.Consumer>
{value => <input value={value} />}
</ThemeContext.Consumer>
createStore
createStore(reducer,[preloadedState],enhancer)根据 Reducer 创建 Store。
reducer:就是从 Reucer 导出的 reducer 函数,负责接收新的state和 Action;
preloadedState:初始时的 state,一般来说是放在 reducer 中,方便管理;
enhancer:这个参数传入一个组合多个 Store 的高阶函数,返回一个新的产生 Store 的函数
connect
connect(mapStateToProps,mapDispatchToProps,[mergeProps],[options])函数是一个高阶函数,负责将 UI 组件,Action,Reducer 连接起来。
-
mapStateToProps(state,[ownProps]):如果一个组件需要监听 Store 内部state的更新,那么必须传入这个函数。这个函数可以接受两个参数,更新后的state以及其他组件传给当前组件ownProps;在接收到新的state以后,mapStateToProps可以在内部操作返回当前组件需要的state,通过props的形式传递到组件内部 -
mapDispatchToProps(dispatch,ownProps):还记得上文说过的吗,Redux 不存在state和props的概念传递数据依赖 Action;mapDispatchToProps函数将返回一个对象,对象的每个字段都是一个函数,在调用这些函数的时候就会生成 Action,然后 Action 会被传送到 Store 内部通过 Reducer 进行处理。dispatch就是生成 Action 的函数,默认情况下,dispatch会通过props注入到组件内部,这样组件内部就可以在交互的过程中产生 Action 触发dispatch事件,然后 Store 就可以获取 Action。 -
mergeProps:额外的传入组件内部的props -
options:一个额外的参数对象,可以设置以下参数:pure: true:默认值就是true,也就是将对组件内部的state进行一个浅比较,避免不必要的根本更新withRef: false:默认值false,保存一个对被被包含的组件实例的引用,该引用通过getWrappedInstance()方法获得。
connect函数会被调用两次:
- 第一次调用,通过将上述两个函数传入到
connect内部以后,connect会生成一个新的高阶函数,新的高阶函数接受组件作为参数,可以生成一个高阶组件 - 第二次调用会生成一个高阶组件
项目的管理
一般来说,最直观的在项目中使用react-redux的方式是利用一个单独的文件夹redux来集中管理数据,在redux目录中,
actions负责生成 Action,这样组件内部可以直接将actions内部导出生成 Action 的函数传递给mapDispatchToProps,然后组件内部就可以通过props获取到生成 Action 的函数,将数据传递给它,例如:
// actions文件夹中负责生成Action的函数
export const addTodo = value => ({
type: 'ADD_TODO',
payload: {
id: ++todoId,
value,
},
});
export const toggleTodo = todoId => ({
type: 'TOGGLE_TODO',
payload: { id: todoId },
});
//组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { connect } from 'react-redux';
import { addTodo } from '../../redux/actions';
class Input extends Component {
state = {
value: '',
};
handleInput = e => {
this.setState({
value: e.target.value,
});
};
handleEnterKeyUp = e => {
if (e.keyCode === 13) {
this.setState({ value: '' });
//获取props注入的生成Action的函数
this.props.addTodo(this.state.value);
}
};
render() {
return (
<input
placeholder="请输入事项"
value={this.state.value}
onChange={this.handleInput}
onKeyUp={this.handleEnterKeyUp}
/>
);
}
}
//直接将生成Action的函数放在对象中传递给connect,简单简洁
export default connect(null, { addTodo })(Input);
reducers负责构建操作state的 Reducer,并生成新的state;各个组件或者页面的 Reducer 可以拆分,然后在index.js中统一使用combineReducers组合
const initState = {
todoList: [],
};
/**
* 接收当前state和Action,根据不同的Action执行不同的操作,然后返回的新的state
* @param {Object} state
* @param {Object} action
*/
export default function(state = initState, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case actionType.add_todo: {
const { id, value } = action.payload;
return {
todoList: [
...state.todoList,
{
id,
value,
isComplete: false,
},
],
};
}
case actionType.set_complete: {
const { id } = action.payload;
const newTodoList = [...state.todoList];
const oldIndex = newTodoList.findIndex(item => item.id === id);
let todoItem = newTodoList[oldIndex];
todoItem.isComplete = true;
newTodoList.splice(oldIndex, 1, todoItem);
return {
todoList: newTodoList,
};
}
default:
return state;
}
}
store只负责根据reducers文件夹导出的 Reducer 生成 Store
import { createStore } from 'redux';
import reducer from '../reducers';
export default createStore(reducer);
- 最后由
Provider对store进行全局共享
import React from 'react';
import { Provider } from 'react-redux';
import store from './redux/store';
export default function() {
return (
<Provider store={store}>
<Root />
</Provider>
);
}
最后就是这样的目录结构:
redux
├─ actions
│ ├─ actionType.js
│ └─ index.js
├─ reducers
│ └─ index.js
└─ store
└─ index.js